ULTRASONIC WELDERS
About Sonic Welding
Ultrasonic welders are a type of advanced welding technology that uses high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to join materials, usually thermoplastics. The process involves the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical vibrations, which are then transmitted through a transducer and focused on the parts being welded. These high-frequency sound waves (typically in the range of 20 to 40 kHz) generate localized heat at the interface of the materials, causing them to soften and bond together. The ultrasonic energy is applied for a very short period, typically between 0.1 and 1 second, resulting in a quick and highly efficient welding process.
One of the main benefits of ultrasonic welding is its precision and speed. The ultrasonic vibrations can be focused on very small areas, allowing for detailed, high-quality welds without the need for additional materials such as adhesives or fasteners. This makes it particularly useful for industries where precision is critical, such as in electronics, medical devices, automotive components, and packaging. ultrasonic welders can also produce clean, strong bonds with minimal thermal impact on surrounding materials, which helps to preserve the integrity of sensitive components.
Another significant advantage of ultrasonic welding is its environmental benefits. Since the process requires no solvents, glues, or other chemicals, it generates less waste compared to traditional methods like adhesive bonding or traditional heat welding. The absence of additional consumables also leads to lower operational costs over time. Furthermore, ultrasonic welding is energy-efficient, as it typically requires less power than other welding methods, making it an eco-friendly solution for manufacturers looking to reduce their environmental footprint.
Finally, the versatility of ultrasonic welding is noteworthy. It can be used to weld a wide range of materials, including different types of plastics, and can also be adapted for complex geometries and intricate designs. Its ability to weld delicate, small parts with minimal thermal distortion is especially beneficial in sectors like electronics and medical device manufacturing, where high-quality, reliable components are essential. The process is also highly scalable, capable of meeting both small-batch production needs and high-volume manufacturing demands.
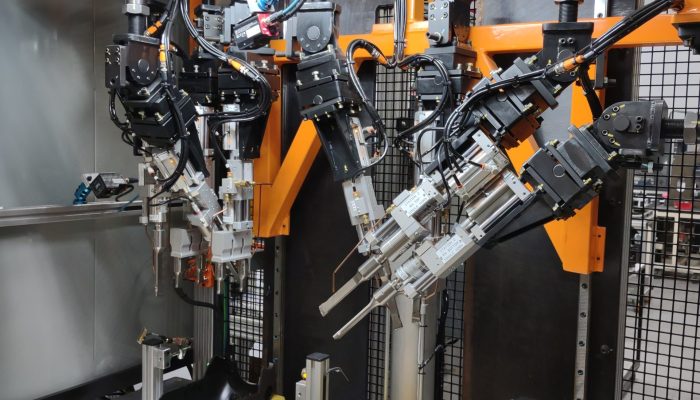

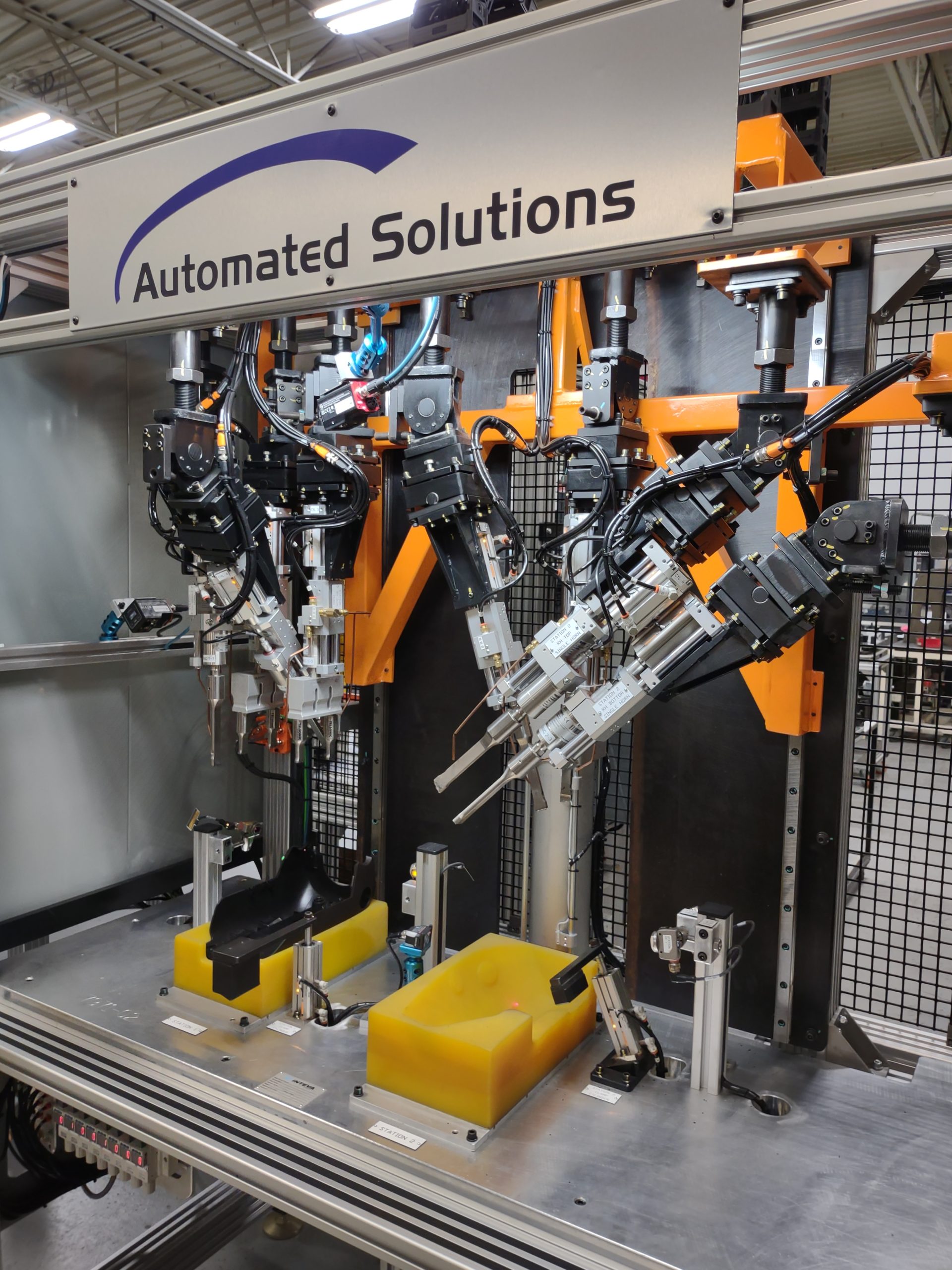
Gallery
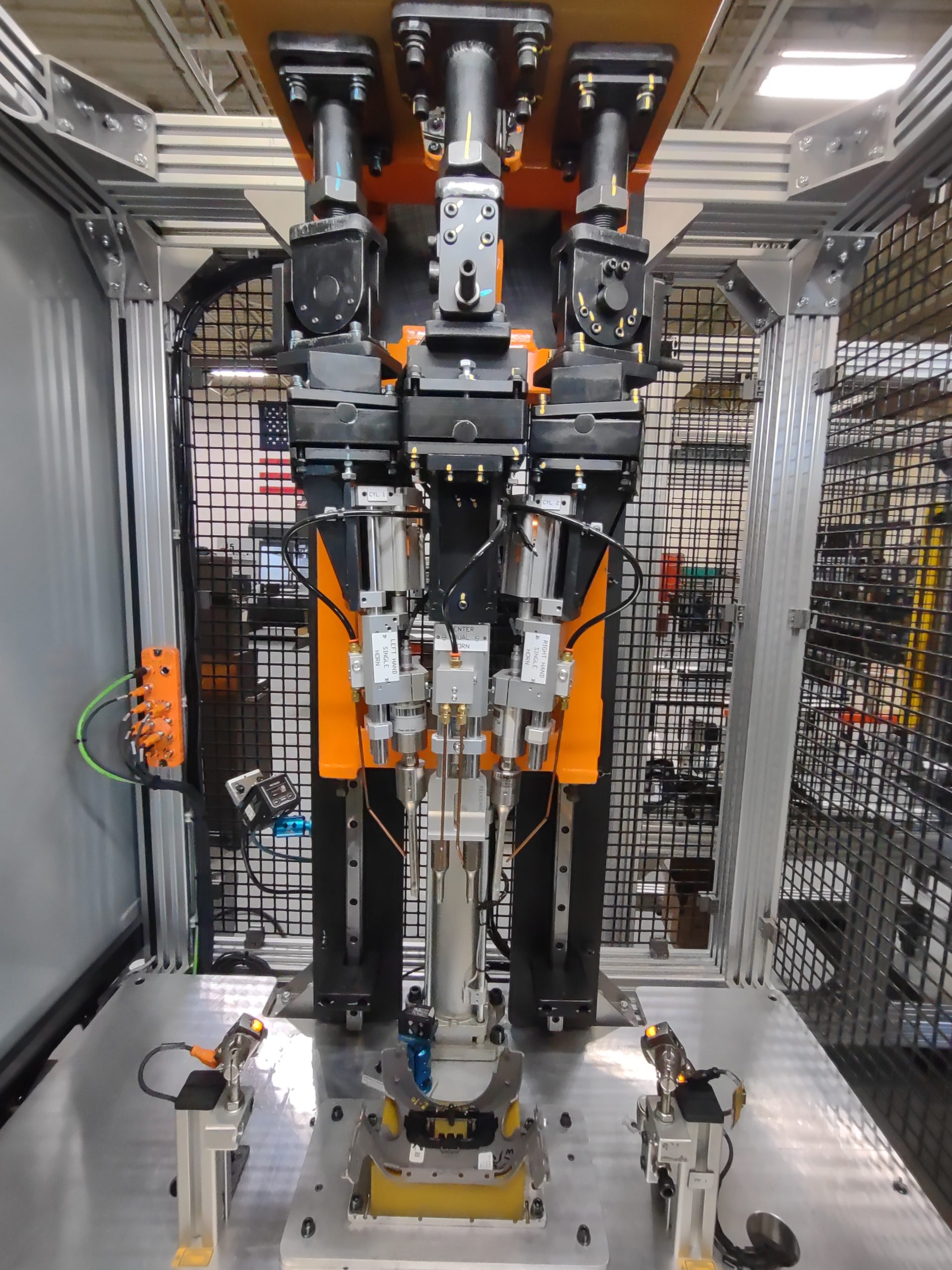
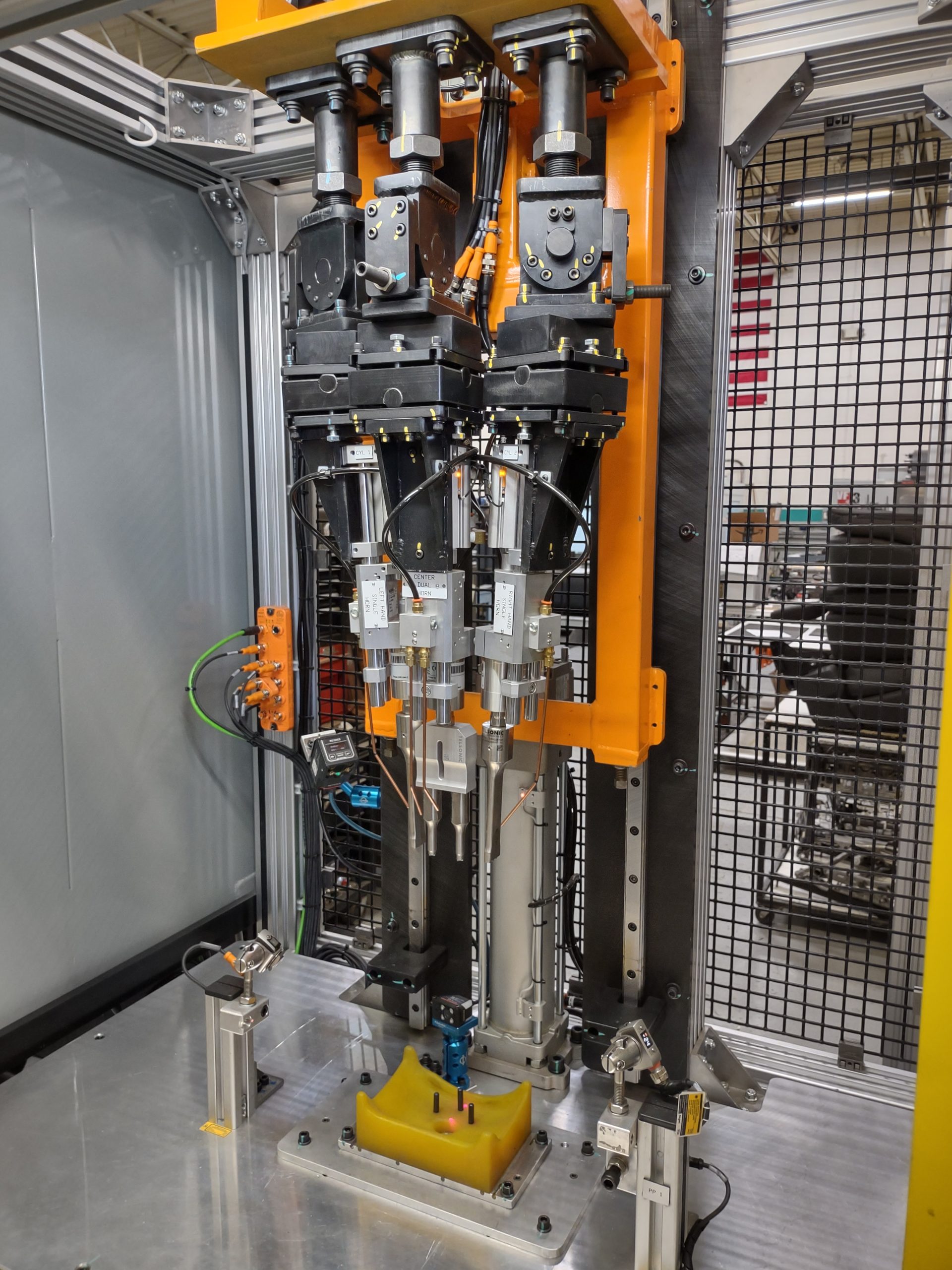
The Welding Process
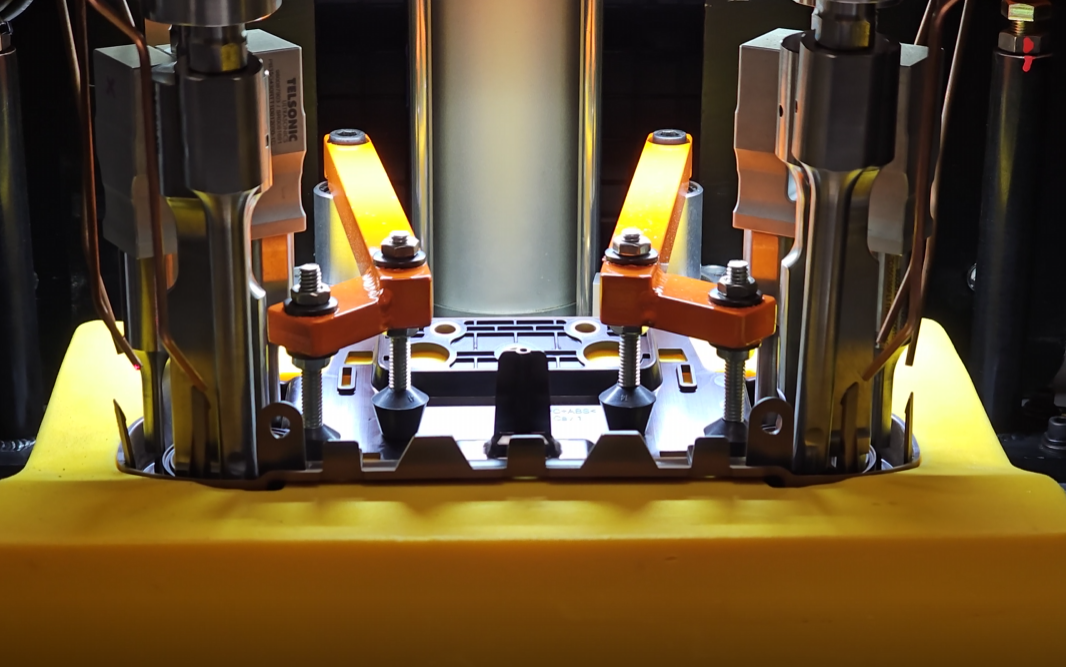


Screens are placed into the nest along with the frame. Then once part presence is verified they are welded into the plastic frame, both posts and tabs are used for adhesion. Once welded the plastic posts resemble a rivet.